Anti-DNAJC17 Rabbit pAb (100 μl)
| Reactivity: | H |
| Applications: | WB |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Full Name: | DNAJC17 rabbit polyclonal |
Gene Name: | DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 17 |
Synonyms: | Dnajc17, FLJ10634 |
Immunogen: | Recombinant protein corresponding to Mouse DNAJC17 |
Isotype: | IgG |
Purity: | Affinity purification |
Predicted MW. | 34 kDa |
Observed MW. | 34 kDa |
Uniprot ID: |
Product Usage Information
Applications | Species | Dilution | Positive tissue |
WB | Human | 1: 1000-1: 2000 | HeLa, NIH3T3, Raji, HepG2 |
Background
The DnaJ family is one of the largest of all chaperone families and has evolved with diverse cellular localization and functions. The presence of the J domain defines a protein as a member of the DnaJ family. DnaJ heat shock induced proteins are from the bacterium Escherichia coli and are under the control of the htpR regulatory protein. The DnaJ proteins play a critical role in the HSP 70 chaperone machine by interacting with HSP 70 to stimulate ATP hydrolysis. The proteins contain cysteine rich regions that are composed of zinc fingers, forming peptide binding domains responsible for chaperone function.
Images
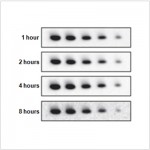
 | Western blot analysis of DNAJC17 (GB112771) at dilution of 1: 1000 |
Storage
| Storage | Store at -20°C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02%sodium azide,100 μg/ml BSA and 50% glycerol. |