Anti-NFkB p105 / p50 Rabbit pAb (100 μl)
| Reactivity: | H |
| Applications: | WB |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Gene Name: | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit |
Synonyms: | DNA binding factor KBF1, EBP 1, KBF1, NF kappa B, NFKB p105, NFKB p50, NFKB1, NFKB1,p105, NFKB1,p105,p50, nfkb1a, NF-κB, NF-κB 1, p105, p50 |
Immunogen: | KLH conjugated Synthetic peptide corresponding to Mouse NFkBp105 |
Uniprot ID: | P25799 |
Isotype: | IgG |
Purity: | Affinity purification |
Predicted MW. / Observed MW. | 105/84/98/40/65/56/44 kDa / 50 kDa |
Product Usage Information
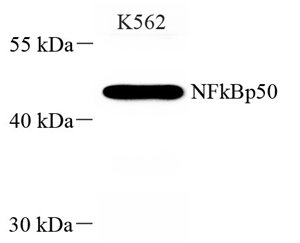
WB | Human | 1: 300-1: 800 | K562 |
Background
NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52 and the heterodimeric p65-p50 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family.
Images
| Western blot analysis of NFkBp105 (GB115431) at dilution of 1: 800 |
Storage
| Storage | Store at -20°C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02%sodium azide,100 μg/ml BSA and 50% glycerol. |