Anti-Kir2.1/BIK Rabbit pAb (100 μl)
| Reactivity: | M,R |
| Applications: | WB |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Full Name: | BIK rabbit polyclonal antibody |
Gene Name: | Inward rectifier potassium channel 2 |
Synonyms: | Inward rectifier K(+) channel Kir2.1, IRK-1, Potassium channel, inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 2, Kcnj2, Irk1 |
Immunogen: | Recombinant protein corresponding to Mouse BIK |
Isotype: | IgG |
Purity: | Affinity purification |
Predicted MW. | 48 kDa |
Observed MW. | 55 kDa |
Uniprot ID: | P35561, Q64273 |
Applications
Applications | Species | Dilution | Positive Sample |
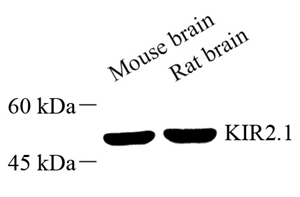
WB | Mouse, Rat | 1: 500-1: 1000 | brain |
Background
KCNJ2, also named as HHBIRK1, HHIRK1, IRK1, KIR2.1, LQT7 and SQT3, belongs to the inward rectifier-type potassium channel family. KCNJ2 probably participates in establishing action potential waveform and excitability of neuronal and muscle tissues. Inward rectifier potassium channels are characterized by a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into the cell rather than out of it. Their voltage dependence is regulated by the concentration of extracellular potassium; as external potassium is raised, the voltage range of the channel opening shifts to more positive voltages. The inward rectification is mainly due to the blockage of outward current by internal magnesium. KCNJ2 can be blocked by extracellular barium or cesium. Defects in KCNJ2 are the cause of long QT syndrome type 7 (LQT7). Defects in KCNJ2 are the cause of short QT syndrome type 3 (SQT3).
Images
|
|
Western blot analysis of KIR2.1 (GB111433) at dilution of 1: 500 |
Storage
| Storage | Store at -20°C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02%sodium azide,100 μg/ml BSA and 50% glycerol. |