Recombinant Anti-Estrogen Receptor alpha Mouse mAb (100 μl)
| Reactivity: | H |
| Applications: | IHC/IF |
| Host Species: | Mouse |
| Clonality: | Monoclonal |
| Gene Name: | Estrogen receptor |
Synonyms: | ER, ER-alpha, Estradiol receptor, Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group A member 1, ESR1, ESR, NR3A1 |
Immunogen: | KLH conjugated Synthetic peptide corresponding to Human ESR1 |
Uniprot ID: | P03372 |
Isotype: | IgG1 |
Purity: | Affinity purification |
Subcellular location: | Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Cell membrane |
Predicted MW. / Observed MW. | 66 kDa / 66 kDa |
Product Usage Information
IHC/IF | Human | 1: 500-1: 1000 | breast cancer |
Background
Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner.
Images
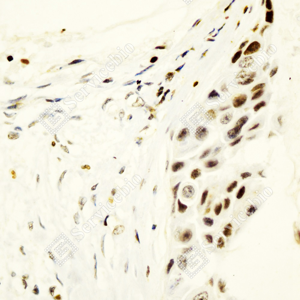
| IHC analysis of Estrogen Receptor alpha(GB151843). |
Storage
| Storage | Store at -20°C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02%sodium azide,100 μg/ml BSA and 50% glycerol. |